DB 테스트 - Mocking vs. Test DB
서론
DB를 테스트하는 방법은 크게 Mocking, TestDB가 있습니다.
Mocking은 실제 DB에 연결하지 않고 DB역할을 하는 가짜 객체에게 요청과 응답을 테스트하는 방법입니다.
TestDB는 실제 DB에 연결하고, 테스트용 데이터베이스와 실제 상호작용하며 테스트하는 방법입니다.
어떤 방법으로 DB를 테스트하는게 좋을지가 이 글의 주제입니다.
본론
TestDB의 가장 큰 장점은 DB에 실제로 연결하고, 테스트 데이터를 실제로 넣어보며 상호작용한다는 것입니다. 이는 애플리케이션 환경과 DB서버 환경이 다름에서 발생하는 여러가지 이슈들을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
이와 관련하여, CRUD 게시판 프로젝트를 진행하며, 레포지토리 단위테스트 중 Java와 MySQL의 Timestamp 부정합 오류를 조기에 발견한 사례가 있어 공유하고자 합니다.
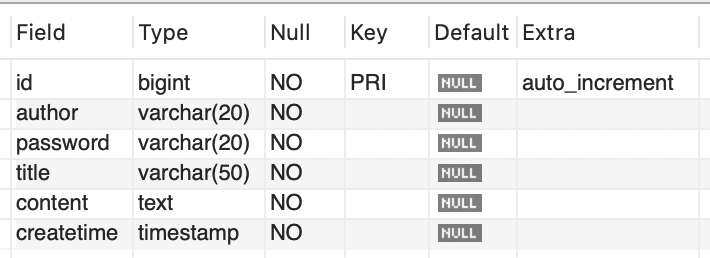
Java의 Board 도메인 객체와 MySQL Board 테이블의 명세는 다음과 같습니다.
public class Board {
private Long id;
private String author;
private String password;
private String title;
private String content;
private Timestamp createTime;
// something
}
테스트 코드와 테스트 결과는 아래와 같고, 테스트 디비에 직접 테스트하였습니다.
@Test
@DisplayName("게시판 조회")
void read() {
// given
testBoard = new Board("익명1", "1234", "제목입니다.", "내용입니다.", new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Board saveBoard = repository.save(testBoard);
Board findBoard = repository.findById(saveBoard.getId());
assertThat(findBoard).isEqualTo(saveBoard);
}

원인: 애플리케이션 환경과 DB서버 환경의 설정 불일치
- 공식문서를 통해, 문제의 원인을 파악할 수 있었는데요. 테이블 Timestamp 컬럼과 Java Timestamp의 나노초 소수점 처리방식을 일치시키지 않았기 때문입니다.
- Java 에서 제공하는 Timestamp 데이터 타입과 MySQL의 Timestamp 컬럼 타입 모두 ms를 지원해줍니다.
- Java는 소수점 자리 처리방식이 default = 2번째 자리입니다.
- MySQL은 소수점 자리 처리방식이 default = 0번째 자리입니다
- 따라서, 테이블을 생성할 때 아래와 같이 명시해주어야 합니다.
이외에, LocalDateTime 등 나노초를 지원하는 모든 라이브러리도 동일합니다.
CREATE TABLE fractest( c1 TIMESTAMP(2) );
INSERT INTO fractest VALUES
('2018-09-08 17:51:04.777');mysql> SELECT * FROM fractest;
+------------------------+
| c1 |
+------------------------+
| 2018-09-08 17:51:04.78 |
+------------------------+
해당 crud프로젝트는 나노초 단위는 필요하지 않아서, 소수점을 처리하지 않는 방식으로 명세를 통일하여 해결했습니다. 애플리케이션 요구사항에 따라 나노초 필요 여부를 판단하고 일치시키면 될 것입니다.
결론
Mock의 경우 애플리케이션 환경과 실제 DB 환경이 다른 경우 발생하는 이슈들에 대한 테스트가 이루어지지 않을 수 있습니다. 따라서,
실제 DB와 테스트를 진행하는 것이 좋을 것으로 생각합니다.
Reference
Java Timestamp 공식문서
Note: This type is a composite of a java.util.Date and a separate nanoseconds value. Only integral seconds are stored in the java.util.Date component. The fractional seconds - the nanos - are separate.
MySQL 11.2.6 Fractional Seconds in Time Values 공식문서
The fsp value, if given, must be in the range 0 to 6. A value of 0 signifies that there is no fractional part. If omitted, the default precision is 0. (This differs from the standard SQL default of 6, for compatibility with previous MySQL versions.)
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/datetime.html
MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 11.2.2 The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP Types
11.2.2 The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP Types The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP types are related. This section describes their characteristics, how they are similar, and how they differ. MySQL recognizes DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP values in several f
dev.mysql.com
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/fractional-seconds.html
MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 11.2.6 Fractional Seconds in Time Values
11.2.6 Fractional Seconds in Time Values MySQL has fractional seconds support for TIME, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP values, with up to microseconds (6 digits) precision: To define a column that includes a fractional seconds part, use the syntax type_name(fsp)
dev.mysql.com
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/sql/Timestamp.html
Timestamp (Java Platform SE 8 )
Converts this Timestamp object to a LocalDateTime. The conversion creates a LocalDateTime that represents the same year, month, day of month, hours, minutes, seconds and nanos date-time value as this Timestamp in the local time zone.
docs.oracle.com
https://lenditkr.github.io/MySQL/fractional-seconds-rouding-problem/
아니 시간도 반올림이 된다고?
니가 지정한 내가 아냐~ - Soo
lenditkr.github.io